کاهش دائمی موهای زائد، نه حذف دائمی موهای زائد!
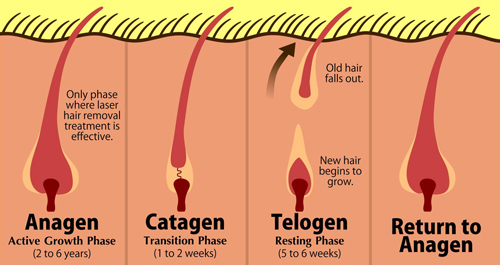
According to Food and Drug Administration permanent hair reduction defined as, “the long-term, stable reduction in the number of hairs regrowing after a treatment regime. The number of hairs regrowing must be stable over a time greater than the duration of the complete growth cycle of hair follicles, which varies from 4 to 12 months according to body location. Past few years enamors lasers have been introduced in cosmetology. Laser wavelength is a key factor influencing treatment efficacy and complication rates. Neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet lasers, alexandrite, diode and other various lasers are in market for hair reduction.
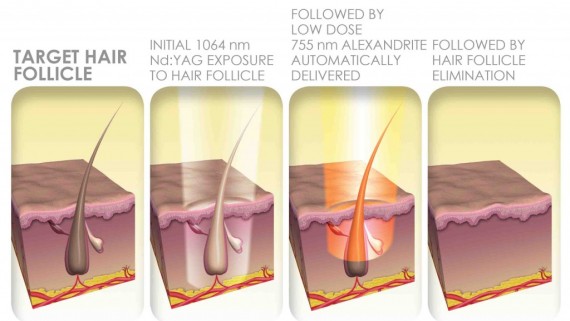
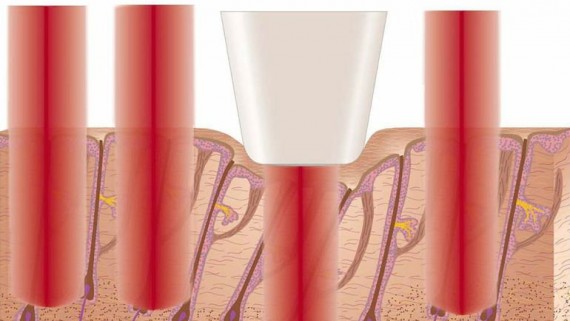
In hair anatomy stem cells in a “bulge” and the dermal papilla are two main structures for hair cycle and reproduction. Diode lasers acts on principal of “selective photothermolysis” and only destroys a small fraction of hairs completely.[1] All lasers including diode selectively absorbed by melanin chromospheres, which cause thermal damage of surrounding structure such as shaft and root.[2] wave length between 700 and 1000 nm are selectively absorb by melanin chromophore. Other competing chromophores (oxyhemoglobin and water) absorb less energy at these wavelengths.[3] According to study 800 nm wave length proved better treatment option than other lasers as it require lesser sessions, less painful, and more effective.[4] Long pulse diode lasers ranges from 800 to 810 nm. There are many companies which are manufacturing machines with different wavelength output such as 800 nm, 808 nm, and 810 nm. Among diode lasers 810 nm seems better wavelength as it penetrates deeper and scatters lesser than 800 nm.[5] Lasers acts on melanin chromophore. Type I and II require higher fluences and small pulse duration while darker skin types (Type IV, V, VI) require less fluences and longer pulse duration to avoid surface skin injury due to absorption of light in the pigmented epidermis, while still causing selective destruction of the underlying pigmented hair follicles.[6]
Contrary to permanent hair reduction subtheraputic fluences of diode laser may induce hair growth called as paradoxical hypertrichosis. This phenomenon is commercially used in lasers combs for androgenic and other type of hair loss. Low level laser therapy (LLLT) also called as soft laser or cold laser. The mechanism of LLLT at the cellular level is based on the absorption of monochromatic radiation by components of the cellular respiratory chain in mitochondria. It increases adenosine triphosphate production and cell division in matrix of hair.[7,8]
Laser hair reduction one of the most common procedures performed by dermatologists all over the world. It is a safe and effective procedure. The term hair reduction should be used instead of hair removal as a significant percentage of hair tends to come repeatedly even after many sessions.



دیدگاه
دیدگاهی ثبت نشده.